How Cells Repair DNA’s Protective Barrier: A pathway to address a rare genetic disorder characterized by rapid aging in children
Researchers at Nano Life Science Institute (WPI-NanoLSI), Kanazawa University, have discovered how a protein called lamin A helps repair the protective barrier around a cell’s DNA. The findings reveal lamin A’s unique role and its potential for treating Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome, a rare disorder that causes premature aging.
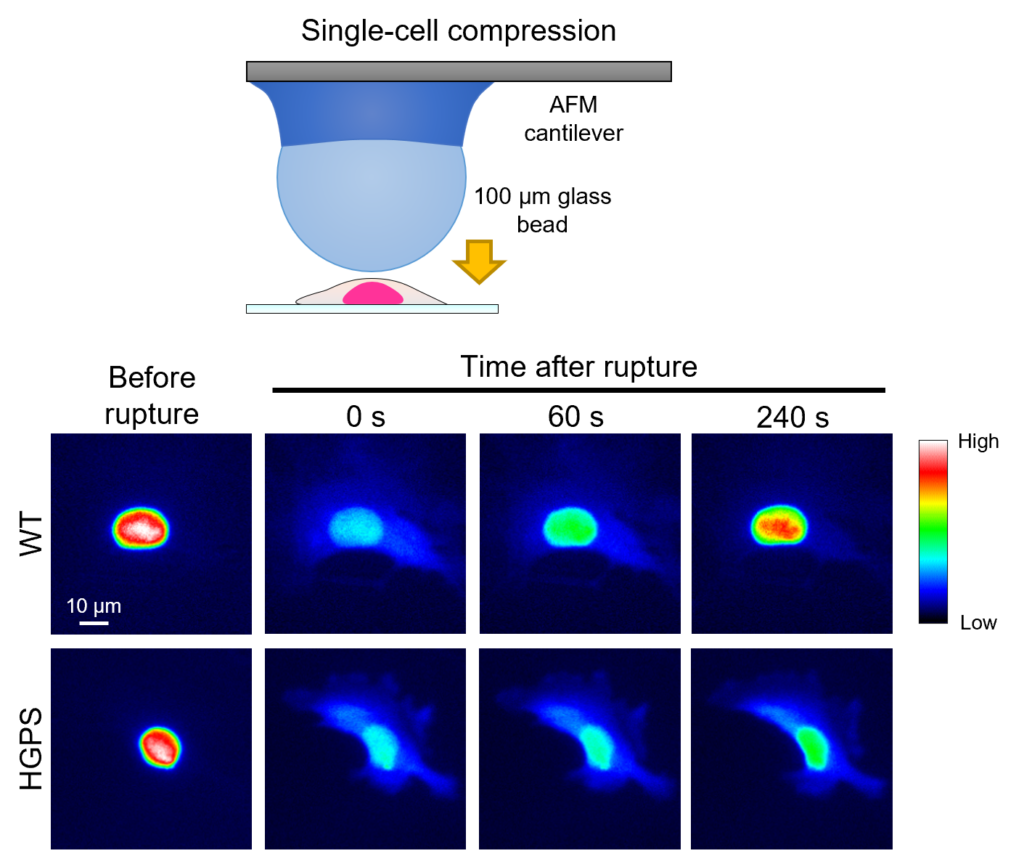
The nuclear envelope (NE) is a vital barrier that protects the cell’s genetic material. It is supported by the nuclear lamina (NL), a fibrous protein network composed of lamins, including lamin A (LA) and lamin C (LC). Mechanical stress or genetic abnormalities can cause ruptures in the NE, exposing the genetic material to damage. While lamin C rapidly accumulates at NE rupture sites to facilitate repair, lamin A exhibits slower and weaker localization.
This slower response poses significant challenges, especially in diseases like Hutchinson–Gilford Progeria Syndrome (HGPS). In HGPS, a mutation in the LMNA gene produces progerin, a defective variant of lamin A that remains permanently associated with the NE and disrupts repair mechanisms (Fig. 1). Because progerin’s impaired mobility reduces the reserve pool available for repair, cellular damage could be further compounded, contributing to accelerated aging symptoms in patients.
An international team of researchers led by Takeshi Shimi at the NanoLSI, Kanazawa University, aimed to solve a critical question: Why does lamin A localize more slowly to NE rupture sites compared to lamin C, and how does this difference impact nuclear stability in both normal and diseased states? Specifically, they sought to understand how lamin A’s unique tail region and the post-translational modifications, such as farnesylation, influence its localization and functionality.
Key Findings
- Lamin A’s Tail Region
The researchers have identified specific sequences in lamin A’s tail region, termed “Lamin A-Characteristic Sequences” (LACS1 and LACS2) that inhibit its rapid localization to rupture sites (Fig.2). - Progerin’s Impact in HGPS
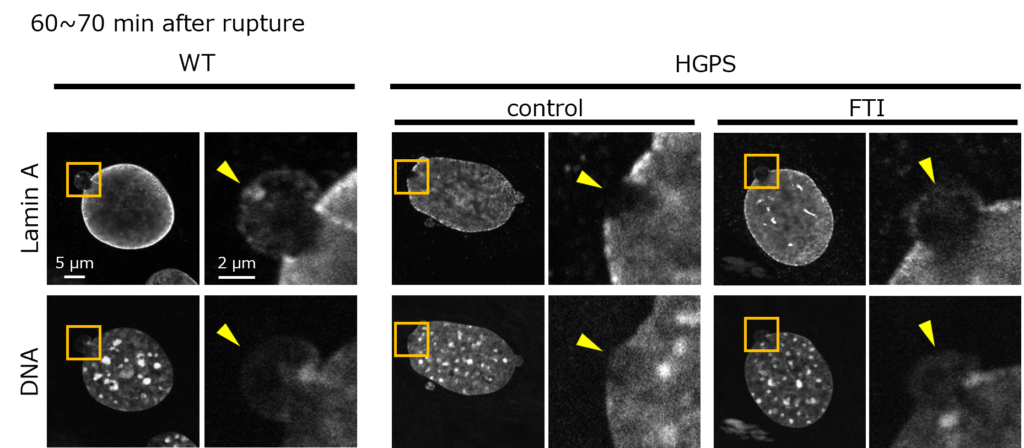
Progerin’s defective structure leads to its permanent retention at the NE, reducing the nucleoplasmic pool of lamin A required for efficient NE repair. This delayed response contributes to nuclear instability and cellular aging. - Therapeutic Potential
A farnesyltransferase inhibitor (FTI), lonafarnib (Zokinvy) improves progerin and lamin A mobility and increase its nucleoplasmic availability, significantly enhancing NE repair in both healthy and HGPS models (Fig.3). This drug is approved in the United States, Europe, and Japan for the treatment of patients with HGPS.
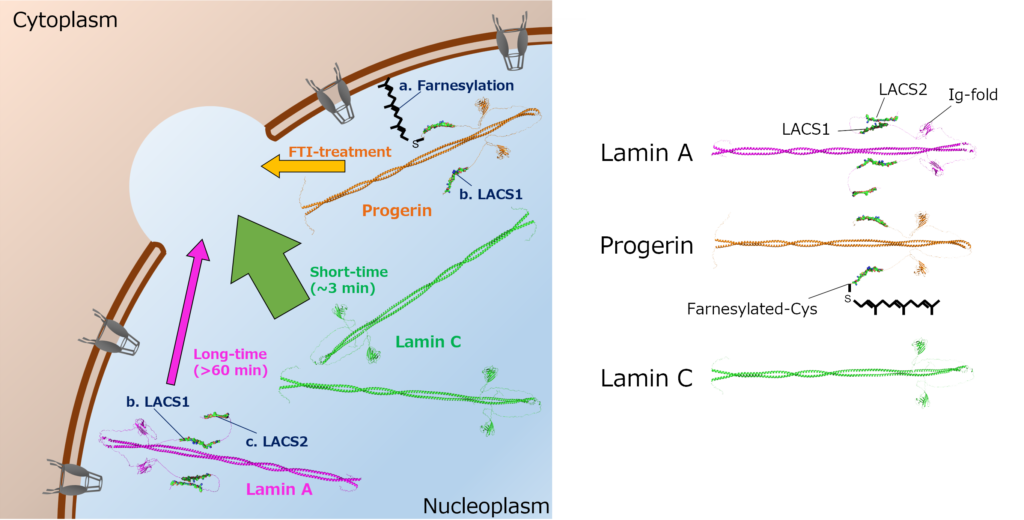
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of the difference in localization to the rupture sites between Lamin A, Lamin C, and Progerin.
“This study bridges a critical gap in our understanding of Lamin A’s role in nuclear repair. It provides actionable insights for developing therapies targeting conditions where nuclear instability is a hallmark, such as HGPS,” say the authors.
Glossary
Nuclear Envelope (NE)
A double membrane that encloses the nucleus, protecting the genetic material.
Nuclear Lamina (NL)
A fibrous network inside the nucleus that provides structural support and regulates gene expression.
Lamin A (LA)
A structural protein in the nuclear lamina critical for maintaining nuclear envelope stability.
Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome (HGPS)
A genetic disorder caused by a mutation in the LMNA gene, leading to the production of progerin, a defective lamin A variant.
Farnesylation
A lipid modification of proteins like Ras, crucial for their localization and function.
Farnesyltransferase Inhibitors (FTIs)
Drugs that block farnesylation, showing promise in restoring progerin and lamin A functionality.
Article
- Title
- Roles of the Lamin A-specific Tail Region in the Localization to Sites of Nuclear Envelope Rupture
- Author
- Yohei Kono, Chan-Gi Pack, Takehiko Ichikawa, Arata Komatsubara, Stephen A. Adam, Keisuke Miyazawa, Loïc Rolas, Sussan Nourshargh, Ohad Medalia, Robert D. Goldman, Takeshi Fukuma, Hiroshi Kimura, Takeshi Shimi
- Journal
- PNAS Nexus
- Publication date
- Nov 21, 2024
- DOI
- 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgae527
- URL
- https://doi.org/10.1093/pnasnexus/pgae527